Generative AI Agents
Podcast
GenAI Agent:
Agent is essentially a program that goes beyond what a standalone GenAI model can do, adds in reasoning, and crucially accesses information outside it’s internal knowledge
- Not just creates text or image, it’s actually trying to achieve a specific goal
- Observes the world around it, takes action based on what it sees. Can even figure out the steps it needs to take to reach that goal even if we haven’t told it exactly what to do
- LLM is the brain
- Cognitive Architecture : Set of components that determine how an agent behaves, how it makes decisions and how it actually takes actions. Components are as below:
- Model : Refers to the language model itself (Heart of the Agent)
- Tools : Give the model the ability to reach beyond their training data and actually affect things. For example, if a model needs to update a customer record or fetch some data from a website, it’d use a tool. It gives the ability to work with external systems
- Orchestration : Control centre of the agent, process that manages how the agent takes in information, how it reasons about the information, how it uses the reasoning to decide what to do next. This process keeps going in cycles until the agent reaches it’s goal
- Plus Points :
- A stand alone model’s knowledge is limited to what it was trained on. But, an agent, since it has access to tools, it can keep learning, can access up to date from the outside world
- Agent can remember the past interactions (The entire history). Can have multi-turn conversations with an agent
- Agents have the built-in intelligence to use the tools strategically (cognitive ability)
How do the Agents Operate ?
Planning → Acting → Observing → Refining
- The Agent’s cognitive architecture allow them to the whole process of taking in information, reasoning about it, making decisions, taking actions and then learning from the results
- The Orchestration layer takes care of the current state of the task and then managing the reasoning and planning
- Prompt Engineering is crucial for guiding the Agent’s thought process
ReAct (Reasoning and Act)
- Framework where we encourage the language model to think step-by-step to reason, then to interact with the environment using tools that’s the ACT part based on what the user is asking
- How it Works ?
- Imagine an user asks the agent a question. “To book a flight”
- The agent following the ReAct framework, will prompt the model to generate the next step, it might ask a clarification question “Where are you flying from ?”
- Then, it might have a thought where it considers the best way to find the flight information, maybe it decides to use a flight API and calls the API, gets the result back from the API and that’s the observation
- The cycle of agent asking questions, thinking things through, using tools goes on until the flight is booked
CoT (Chain Of Thought)
- Getting the model to think through the problem in a very structured way
- We guide the model to explain it’s thought process step by step
Tools
They connect the model to the outside world to external systems and data sources to do amazing things. Tools available for google models are as follows:
-
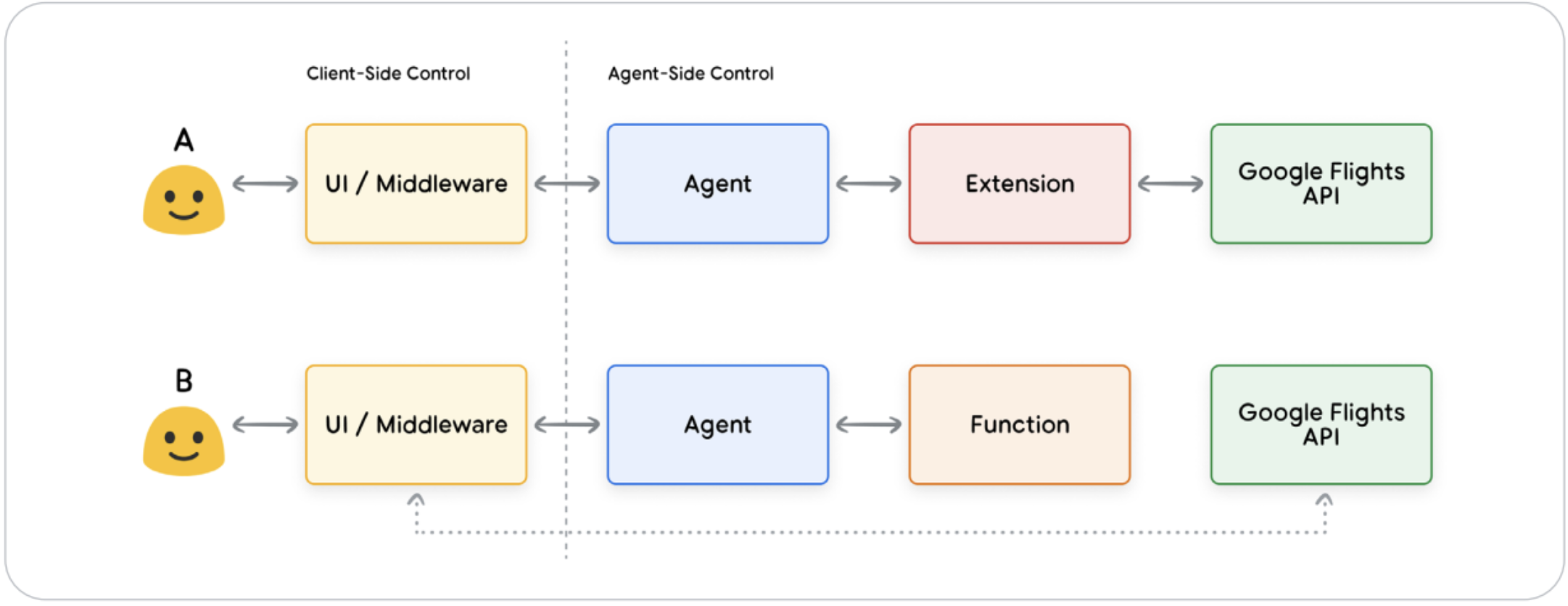
Extensions Standardized way to connect an agent to an API. We give the agent a few examples of how an API should be used, and it learns from the examples. Extensions are developed independently, but are included in the agent’s configurations. At Run-time, the agent can actually look at the user’s query and choose the most appropriate extension based on built-in examples
-
Functions In agent world, the language model decides when to use each function and it figures out what arguments to give it based on the function specifications. We can have API calls inside the function. Can be used in cases where we have asynchronous tasks
Functions are executed on the client side, whereas extensions run on the Agent side. In cases where the API requires some authentication that the agent doesn’t have, we user function so that the client provides that Authentication
- Data Stores
They give agents access to information that’s Dynamic, up-to date and relevant to the current context. The agent can access external data sources like databases or apis to get the most current information.
- Let’s say we need to feed in some new documents to our agent, we can just give those documents to the Data Store (Vector Databases), it converts them into a format that the agent can understand. Then, the agent can query the Data Store to get the information it needs
- One of the most powerful applications of Data Stores is RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) or RA. It’s a technique where we give the language model access to a huge external knowledge base from which the agent can answer queries
Enhancing model performance with targeted learning
We need to make the models choose the right Tools when generating output. Here are some approaches to help the model gain a basic knowledge on it:
- In-Context Learning : Give the model a prompt, relevant tools, and some few-shot examples at inference time which allows it to learn ‘on-the-fly’ how and when to use specific tools for a specific task
- Retrieval based In-Context Learning : This technique dynamically populates the model prompt with the most relevant information, tools, and associated examples by retrieving them from external memory. An example of this would be the ‘Example Store’ in Vertex AI extensions or the data stores RAG based architecture
- Fine-tuning based Learning : In-depth training of the model for a specific task (By training the model on data specific to certain domain with specific examples prior to inference)
TIP
Google’s Vertex AI provides everything we need to build, deploy and manage Agent applications